目前,有三种实现个性化搜索引擎的方法。
- Topic-based personalization
- Long-term vs. short-term personalization
- Personalization for typical vs. atypical information needs
基本逻辑:
- Representation: 描述用户的兴趣/偏好
- Learning: 从数据中学习兴趣/偏好
- Ranking: 在检索算法中使用兴趣/偏好
Topic-based personalization
假设: 用户的长期兴趣(high-level topics)可以从训练数据中得到
预处理:
- 在建立索引前,每篇文档都被分配了 [0…n] 之间的某个类别;
- 在建立索引的时候,类别被当作 feature 或者 metadata 保存起来
User representation:
- 根据用户的长期检索历史对用户建模
- 用户模型是在类别标签上的一个概率分布
arts/movies: 1.1%, arts/television: 0.2%, arts/music: 2%, … - 第 n 个用户的训练数据: p (q1, c1), p(q1, c2), … p(q2, c1) …
p(qi, cj) = p(d is clicked & d in category cj | q)
对排序列表进行 rerank,top n 的文档是两个分数的组合:
- 原始文档分数
- 文档类别和用户兴趣类别的匹配分数
Bing 用 25 天的数据,20 天数据做训练数据,5 天数据做测试数据,一共 102,417 条查询和 54,581 个用户,实验结果:
Long-term vs. short-term personalization
个性化可以基于三种类型的信息:
- Historic: 从用户长期的检索记录中获得的信息
- Session: 用户一个 search session 的信息
- Combination of historic and session: 两者合并的信息
可以把这三方面的信息看作用户历史记录的三个不同的 view。
Features:
View features
- Cosine between view and document topic categories
- Cosine between matching queries (and subsets, and supersets)
and document topic categories - url click count
- url click counts for matching queries (and subsets and
supersets) - Number of queries
- Number of sessions with this query
- Number of subset queries
- Number of superset queries
Query features
- Ambiguity measures: Click entropy, topic entropy
– How much do people click on different pages or topics for
this query? - Difficulty measures: Position in session, length, frequency
- Document rank (not personalized)
User profile:
- User topic entropy
- User query (and subset and superset) entropy
- User position entropy, user query position entropy
实验:
- 特征:每个 view 有 38 个特征,一共 102 个特征
- 数据集:2011年 7-8 月的搜索日志
- 方法:对原始结果集的前 10 篇文档重新排序,用 LambdaMART 算法(pairwise LeToR),然后进行相关性评估。
Value of each view: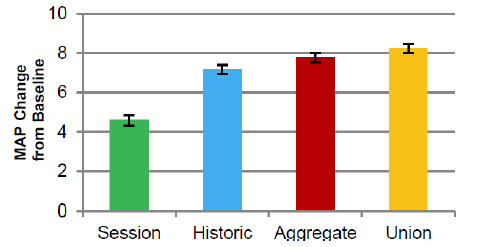
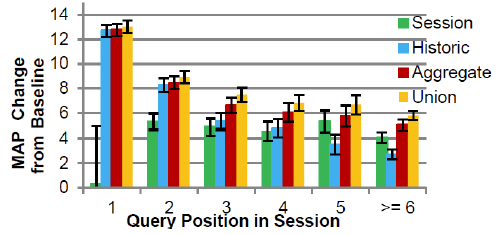
Effect of personalization: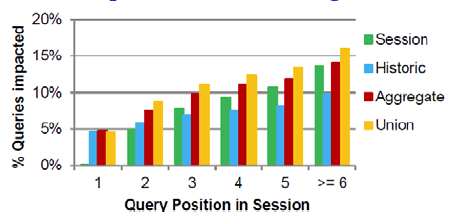
结论:
- Historic 信息在 session 早期的作用比较大
- Session 信息在 session 晚期的作用比较大ssion
- Personalization 在 session 晚期的作用越来越弱
- 可能是因为用户的查询语句更加优化了 - Personalization 在 session 晚期能够影响更多的 query
Personalization for typical vs. atypical information needs
很多个性化的技术假定 user profile 很少变化,然而当用户搜索 atypical 信息时就有问题了。
Detect atypical sessions:
- 创建 long-term user profile
- 衡量 profile 和 session 的 divergence
- Divergence of each session feature from this user’s historical norms
- Cosine distance between session and historical vocabularies
- Cosine distance between session and historical topic categories
然后收集特征,继续按之前 Long-term vs. short-term personalization 的方法来进行实验,最有效的特征: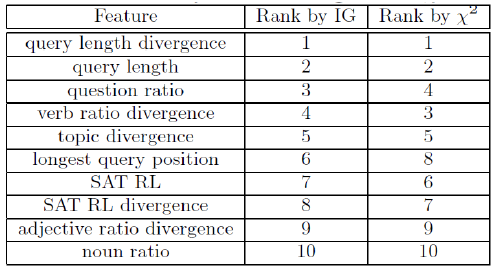
待更新。

